The thermal processing industry continues to evolve with significant advancements in calcination equipment. Modern manufacturing facilities demand reliable, efficient systems that deliver consistent results while minimizing operational costs. Among these critical systems, rotary kilns stand as the backbone of numerous industrial processes, from cement production to chemical manufacturing.
Understanding the technology behind these massive cylindrical systems helps industries make informed decisions when selecting equipment partners. This comprehensive guide examines the latest developments in calcination technology and what sets leading manufacturers apart in today’s competitive market.
Understanding Industrial Rotary Kiln Systems
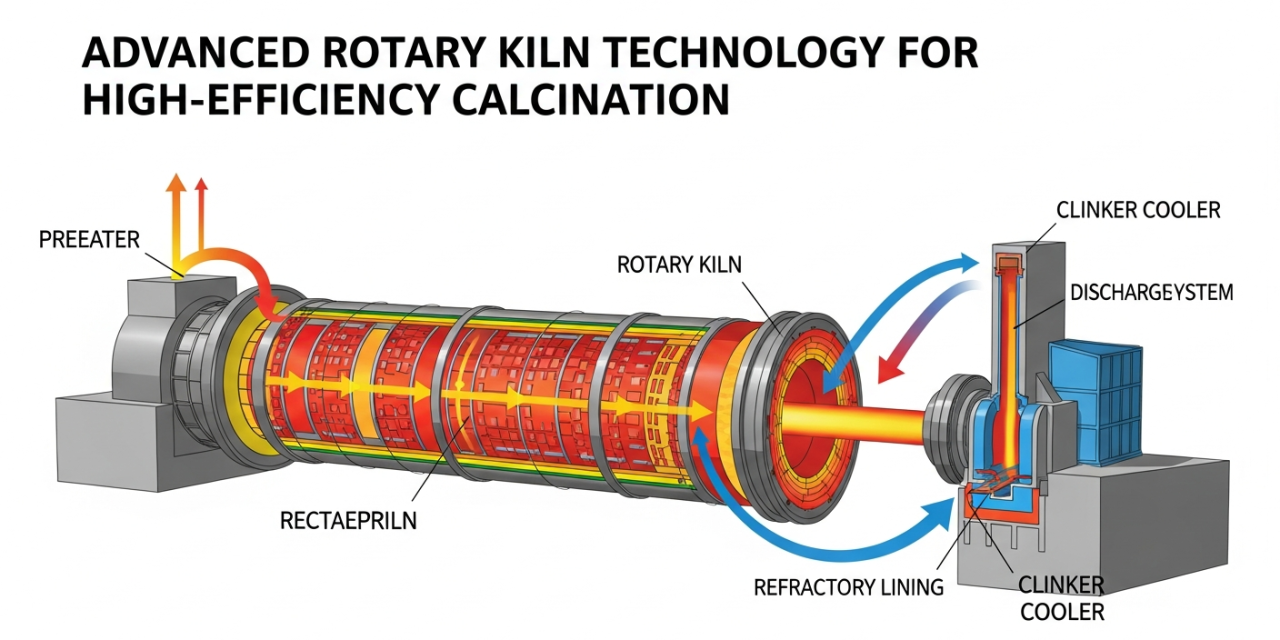
An industrial rotary kiln operates as a cylindrical vessel that rotates slowly around its longitudinal axis, facilitating continuous thermal processing of materials. Raw materials enter at the elevated end and progressively move toward the discharge end, experiencing controlled temperature variations throughout their journey.
The fundamental design consists of a steel shell protected by refractory lining materials. As the cylinder rotates at controlled speeds, materials tumble and mix, ensuring uniform heat exposure. This rotation mechanism, combined with precise temperature control, enables complete calcination of various materials including limestone, dolomite, bauxite, and numerous chemical compounds.
Modern systems incorporate sophisticated control mechanisms that monitor multiple parameters simultaneously. Temperature sensors positioned at various points track thermal profiles, while speed controllers maintain optimal rotation rates. Material flow sensors ensure consistent feeding, preventing overloading or underutilization of kiln capacity.
The refractory lining plays a crucial role in system performance. Multiple layers of specialized materials protect the steel shell while maintaining thermal efficiency. Inner layers withstand extreme temperatures and chemical reactions, while outer layers provide insulation. Regular maintenance and strategic replacement of refractory materials extend equipment lifespan significantly.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Rotary Kiln Manufacturer
Selecting an experienced rotary kiln manufacturer directly impacts operational success, production efficiency, and long-term profitability. Established manufacturers bring extensive engineering knowledge, proven design methodologies, and comprehensive understanding of industry-specific requirements.
A reputable rotary kiln manufacturer invests continuously in research and development, incorporating technological innovations that improve thermal efficiency and reduce energy consumption. These manufacturers maintain state-of-the-art production facilities equipped with precision machining centers, automated welding systems, and rigorous quality control laboratories.
The design phase requires detailed analysis of material characteristics, production capacity requirements, available fuel sources, and site-specific conditions. Experienced manufacturers conduct thorough feasibility studies, providing customized solutions rather than standardized products. This tailored approach ensures equipment matches specific application requirements perfectly.
Manufacturing quality directly affects equipment reliability and lifespan. Leading manufacturers follow stringent quality protocols, including material traceability, non-destructive testing, dimensional verification, and performance testing. International certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ASME standards for pressure vessels validate manufacturing excellence.
Beyond manufacturing, comprehensive support services distinguish exceptional manufacturers from average suppliers. Pre-installation training, commissioning assistance, operational troubleshooting, and planned maintenance programs ensure sustained high performance throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Key Features of Advanced Calcination Technology
Modern calcination systems incorporate numerous technological advancements that separate contemporary equipment from traditional designs. Variable frequency drives enable precise control of rotation speeds, allowing operators to optimize residence time based on material properties and processing requirements.
Advanced burner systems represent significant technological progress. Multi-channel burners provide superior flame control, adjusting fuel-air ratios dynamically to maintain optimal combustion conditions. Some systems incorporate oxygen enrichment capabilities, intensifying combustion and reducing fuel consumption while maintaining required temperatures.
Process automation has revolutionized kiln operations. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) manage all system functions, from material feeding to temperature control and discharge rates. Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) provide intuitive operator control panels, displaying real-time data and enabling rapid response to process variations.
Heat recovery systems capture thermal energy from exhaust gases, redirecting it to preheat incoming materials or generate steam for auxiliary processes. Preheater towers, particularly in cement applications, dramatically improve overall thermal efficiency by utilizing waste heat effectively.
Emissions control technologies address environmental compliance requirements. Electrostatic precipitators, baghouse filters, and selective catalytic reduction systems minimize particulate matter and gaseous emissions. These systems ensure operations meet stringent environmental regulations while maintaining production efficiency.
Applications Across Multiple Industries
The versatility of rotary kiln technology makes it indispensable across diverse industrial sectors. Each application presents unique challenges requiring specialized engineering approaches and customized equipment configurations.
Cement Manufacturing
Cement production represents the largest application for rotary kilns globally. The clinkering process transforms raw materials including limestone, clay, and iron ore into cement clinker at temperatures approaching 1450°C. Modern cement kilns incorporate preheater towers and precalciner systems, significantly improving thermal efficiency compared to traditional long dry kilns.
Lime Production
The lime kiln converts limestone (calcium carbonate) into quicklime (calcium oxide) through thermal decomposition. This endothermic reaction requires careful temperature control and sufficient residence time. Lime finds applications in steel manufacturing, water treatment, construction, agriculture, and chemical processing industries.
Chemical Processing
Chemical industries utilize rotary kilns for various calcination and thermal treatment applications. Alumina production from bauxite, titanium dioxide manufacturing, activated carbon production, and catalyst preparation all rely on precise thermal processing capabilities that rotary kilns provide.
Metallurgical Applications
Metal recovery operations employ rotary kilns for ore roasting, direct reduction processes, and waste recovery. The equipment handles aggressive materials and extreme temperatures while maintaining consistent product quality. Specialized metallurgical designs incorporate features addressing corrosive environments and specific material handling challenges.
Environmental Remediation
Hazardous waste treatment facilities use rotary kilns for contaminated soil remediation and waste incineration. High temperatures and controlled residence times ensure complete destruction of organic contaminants. Sophisticated emissions control systems prevent environmental discharge of harmful substances.
The Growing Market for Rotary Kiln in India
India’s industrial expansion has created substantial demand for advanced thermal processing equipment. The government’s focus on infrastructure development, combined with manufacturing sector growth, positions the rotary kiln in India market for continued expansion.
Several factors drive this growth trajectory. Cement consumption increases with urbanization and construction activity. Steel industry expansion requires additional lime production capacity. Chemical manufacturing diversification creates new applications for specialized calcination equipment.
India’s commitment to environmental sustainability influences equipment selection criteria. Industries prioritize fuel-efficient systems with low emissions profiles. Modern designs incorporating alternative fuel capabilities and advanced pollution control systems align with regulatory requirements and corporate sustainability goals.
The “Make in India” initiative has strengthened domestic manufacturing capabilities. Local rotary kiln manufacturer in India operations combine international technology with indigenous engineering expertise, delivering world-class equipment at competitive prices. This localization reduces import dependency, improves delivery timelines, and simplifies after-sales support.
Selecting a Reliable Rotary Kiln Supplier in India
Choosing the right rotary kiln supplier in India requires careful evaluation across multiple dimensions. Technical competence forms the foundation of supplier selection. Prospective partners should demonstrate proven experience designing and manufacturing kilns for specific applications.
Project portfolio review provides insights into supplier capabilities. Examining completed installations, speaking with existing customers, and visiting operational sites reveal practical equipment performance and supplier reliability. References from similar industries offer particularly valuable perspectives.
Manufacturing infrastructure assessment helps evaluate production capabilities. Modern facilities with advanced machining equipment, automated fabrication systems, and comprehensive testing capabilities indicate serious manufacturing commitment. Quality certifications validate manufacturing processes and material control systems.
Engineering support capabilities extend beyond initial equipment supply. Detailed process engineering, computational modeling for performance optimization, and customization abilities distinguish exceptional suppliers from equipment vendors. Access to experienced engineers who understand application nuances ensures optimal system design.
After-sales service infrastructure significantly impacts long-term satisfaction. Local service presence, spare parts availability, technical helpline access, and preventive maintenance programs minimize operational disruptions. Suppliers offering comprehensive service contracts provide valuable peace of mind for facility managers.
Financial stability and business longevity matter for long-term partnerships. Established companies honor warranty commitments, support customers through equipment lifecycles, and maintain parts availability for older installations. Industry reputation, customer retention rates, and financial health indicators help assess supplier reliability.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Economics
Fuel costs represent significant operational expenses for calcination processes. Modern technology focuses intensively on thermal efficiency improvements that reduce energy consumption per unit of production.
Insulation optimization through advanced refractory materials minimizes heat losses. Multi-layer refractory systems with specialized materials for different temperature zones provide superior thermal performance. Some manufacturers incorporate external insulation that further reduces shell heat losses.
Combustion optimization maximizes fuel utilization efficiency. Advanced burners achieve complete combustion with minimal excess air, reducing waste heat in exhaust gases. Real-time monitoring of oxygen levels and burner adjustments maintain optimal combustion conditions continuously.
Heat recovery systems represent major efficiency improvements. Counter-current heat exchange between incoming materials and exhaust gases significantly reduces fuel requirements. Preheater systems in cement applications can reduce fuel consumption by 40-50% compared to traditional designs.
Alternative fuel utilization provides economic and environmental benefits. Modern kilns accommodate various fuel sources including coal, natural gas, fuel oil, biomass, and refuse-derived fuels. This flexibility allows operations to select most economical fuel sources while reducing dependence on conventional fossil fuels.
Process optimization through data analysis identifies efficiency improvement opportunities. Historical operational data analysis reveals optimal parameter combinations for different materials and operating conditions. Continuous improvement methodologies systematically address inefficiencies and operational losses.
Maintenance Best Practices for Extended Equipment Life
Systematic maintenance approaches maximize equipment availability and extend operational lifespan. Predictive maintenance strategies identify potential issues before equipment failures occur, minimizing unplanned downtime and repair costs.
Refractory management constitutes critical maintenance focus. Regular inspections assess lining condition, identifying areas requiring attention. Infrared thermography detects hot spots indicating refractory thinning or damage. Strategic refractory replacement scheduling minimizes production interruptions while preventing catastrophic failures.
Mechanical component maintenance includes drive systems, support rollers, thrust rollers, and sealing systems. Vibration analysis detects bearing wear and alignment issues early. Lubrication programs follow manufacturer specifications, preventing premature component wear. Regular alignment checks ensure proper load distribution across support systems.
Electrical and control system maintenance ensures reliable operation. Calibration programs verify sensor accuracy and control loop performance. Software backups protect against control system failures. Spare parts inventory for critical electrical components enables rapid repair when issues occur.
Operator training programs develop workforce competencies essential for optimal equipment operation. Training covers operational theory, control system operation, routine maintenance procedures, troubleshooting techniques, and emergency response protocols. Well-trained operators recognize abnormal conditions promptly and implement appropriate corrective actions.
Documentation systems track maintenance activities, component replacements, and operational parameters. This historical data informs maintenance planning, identifies recurring issues, and supports root cause analysis when problems occur. Digital maintenance management systems streamline documentation and improve maintenance efficiency.
Technological Innovations Shaping Future Development
The calcination equipment industry continues evolving with several technological trends influencing future designs. Understanding these trends helps industries anticipate future capabilities and plan strategic equipment investments.
Digital Integration
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) sensors provide unprecedented operational visibility. Continuous monitoring of numerous parameters enables real-time performance analysis and predictive analytics. Cloud-based platforms aggregate data from multiple installations, enabling performance benchmarking and best practice identification.
Artificial Intelligence Applications
Machine learning algorithms analyze operational data to identify optimal parameter combinations. These systems learn from historical performance, continuously refining control strategies. Artificial intelligence applications predict maintenance requirements, optimize fuel consumption, and improve product quality consistency.
Advanced Materials
New refractory materials withstand higher temperatures and more aggressive chemical environments. Nano-engineered materials provide superior insulation properties in thinner cross-sections, reducing kiln mass and thermal inertia. Advanced coatings extend refractory lifespan and improve resistance to chemical attack.
Modular Design Approaches
Modular construction methodologies facilitate phased capacity expansion and technology upgrades. Standardized components simplify maintenance and reduce spare parts inventory requirements. Modular designs enable factory assembly of major sections, reducing on-site construction time and improving quality control.
Enhanced Environmental Performance
Next-generation systems incorporate advanced emissions control technologies as integrated design elements rather than add-on systems. Low-NOx burners, staged combustion, and selective non-catalytic reduction minimize nitrogen oxide formation. Advanced particulate control and gas scrubbing systems ensure compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
Investment Considerations and Financial Planning
Capital equipment investments require thorough financial analysis and strategic planning. Understanding total cost of ownership helps evaluate alternatives and justify investments to stakeholders.
Initial Capital Costs
Equipment purchase price represents only one component of total investment. Installation costs including civil works, electrical infrastructure, material handling systems, and auxiliary equipment can equal or exceed equipment costs. Comprehensive project budgeting accounts for all capital expenditure components.
Operating Cost Analysis
Fuel consumption dominates operating expenses for most calcination applications. Comparative analysis of fuel efficiency between equipment options reveals long-term cost implications. Maintenance costs, including refractory replacement and mechanical component servicing, require realistic estimation based on manufacturer data and industry experience.
Productivity and Quality Benefits
Modern equipment typically offers higher production capacity and improved product quality compared to older systems. Quantifying revenue benefits from increased capacity and premium pricing for superior products strengthens investment justification. Reduced product variability and lower rejection rates provide additional economic benefits.
Financing Options
Equipment financing through manufacturer programs, leasing arrangements, or traditional bank financing affects project economics. Government incentive programs supporting industrial modernization or environmental improvements may provide subsidized financing or tax benefits. Comprehensive evaluation of financing alternatives optimizes capital structure.
Risk Assessment
Technical risks related to equipment performance, operational risks from maintenance requirements, and market risks from demand fluctuations require evaluation. Performance guarantees from manufacturers mitigate technical risks. Comprehensive service agreements reduce operational risks. Market analysis and demand forecasting inform risk assessment.
Conclusion
Advanced rotary kiln technology represents a critical investment for industries requiring high-efficiency calcination capabilities. The continuous evolution of these systems reflects the demands of modern industrial processes requiring reliable, efficient, and environmentally responsible thermal processing solutions.
Success in implementing these sophisticated systems depends significantly on partnering with experienced rotary kiln manufacturer companies who understand both the technology and specific application requirements. The growing capabilities of rotary kiln supplier in India operations position the country as an important source for world-class thermal processing equipment.
Contact Shalimar Engineering today to discuss your rotary kiln requirements and get customized solutions for your production needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a rotary kiln and how does it function in industrial applications?
A rotary kiln is a large, rotating cylindrical vessel used for high-temperature thermal processing. Materials move gradually through the cylinder as it rotates, ensuring uniform exposure to heat. This controlled environment supports calcination, pyroprocessing, thermal decomposition, and material transformation across cement, lime, chemical, and metallurgical industries.
2. Which industries rely most on rotary kiln technology?
Rotary kilns are essential in sectors such as cement manufacturing, lime production, chemical processing, metallurgy, environmental remediation, and waste treatment. Each industry uses specific kiln configurations designed to suit material behavior, temperature requirements, and process goals.
3. Why is selecting the right rotary kiln manufacturer important?
The manufacturer determines the performance, reliability, and operational efficiency of the kiln. An experienced supplier provides engineering expertise, quality manufacturing, precise customization, robust testing, and dependable after-sales support. These factors directly influence production output, energy efficiency, maintenance costs, and equipment longevity.
4. What features define advanced calcination technology in modern rotary kilns?
Current systems integrate automated controls, variable frequency drives, high-efficiency burners, oxygen-enrichment options, heat-recovery units, and advanced refractory materials. These enhancements improve fuel efficiency, temperature stability, emissions control, and overall thermal performance.
5. How important is refractory lining quality in rotary kiln operations?
Refractory linings safeguard the kiln shell from extreme temperatures and chemical reactions. High-quality linings maintain thermal efficiency, reduce heat loss, and prolong equipment life. Regular inspection and replacement schedules are essential for continuous and safe operations.